District Profile
A) Brief description of the district
Buxar district is located in 25o 32'51.10”Nand 83o58'33.61” E. The district, Buxar has two subdivisions, 11 blocks, 291 panchayats and 1134 villages. It covers an area of 1620 Km2 and a population of 14.02 lakh (2011 census). Dumraon and Buxar blocks have sizeable urban population while rest all blocks has only rural population. Males comprise 53 % of the population while females comprise the rest. The average literacy is 72%. Seventy seven percent males and 59% females are literate. Situated on the brink of the holy river Ganges, Buxar is the second Benares.
B) Social and economic profile
Agriculture is the mainstay of economy keeping 59 % of the population gainfully employed. It has a net cultivated area of 142,931 ha. Around 70% of the cultivable land is cultivated more than once. The district has majority rural population (90.8 %) and some urban population (9.2%).
There are 1.92 lakh households with an average size of 7 members. The density of population is 864 persons per sq.km. Sex ratio is 899 males per 1000 female population. The population growth rate is 2.5% and the infant mortality (per 1000) is 65. The scheduled caste population is 14% and Scheduled tribes comprise meager 0.6%.
During Last 05 Year 2012-17
| S.N. | Occupation | Persons | Males | Females |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | Cultivators | 147213 (36.1) | 129887 (39.5) | 17326 (21.9) |
| ii | Agricultural Laborers | 163857 (40.15) | 115449 (35.1) | 48408 (61.3) |
| iii | Workers in Household Industries | 16019 (3.92) | 11259 (3.4) | 4760 (6.0) |
| iv | Other Workers | 81097 (19.87) | 72619 (22.1) | 8478 (10.7) |
(Figures in parenthesis represent percentage of population)
Buxar excels in rice production also known in Bihar as rice bowl i.eDhankakatora. Irrigation is provided to 53 % of the cultivable area under Kharif and 47 % in Rabi season. One major canal of Sone command is the main source of irrigation to the farmers alongwith its subsidiary channels and tubewells. Other crops are maize, jowar, bajra, pulses and oilseeds. Some farmers are getting their income through Beekeeping. The district has sizable under mango cultivation.The animal Husbandry and Dairying activities comprise rearing of cattle and buffaloes, Shahbadi breed of sheep and Bengal goats. Pigs are generally indigenous. Most of the farmers (77%) are marginal or small and resource poor. They are engaged in sheep and goat, poultry and piggery. Milk is sold locally as well as supplied to the Shahabadi milk collection centre at Dumraon. Sheep is used both for meat and coarse blankets and goat for chevon. The district is famous for horticulture and vegetable production.Chausa mangoes are well known. In vegetable production cabbages, cauliflower, tomatoes, onions, potato, cowpea, brinjal and cucurbitaceous vegetables are being sold locally and at Benares wholesale vegetable market. Paddy which was earlier sold to the rice mills is at present procured by the state food corporation or Primary Agriculture Credit Societies (PACS) under minimum support price (MSP). Similar is the case with wheat.
C) Technological Profile
The use of technology and other major inputs are low as 77% of the land holding and 56% of the cultivable land of the district are held by marginal/small farmers who are generally resource poor. Since rice is the main crop the farmers have adopted the farm mechanization which is better than most of the other districts in the state. Cultivation of sugarcane is still negligible but agronomic conditions are suitable for its cultivation. The use of High Yielding Varieties (HYV) seeds and seed replacement is very low which makes it necessary to promote seed production. The use of micronutrients is low. In the last three years, the KVK and the district line department has increased the usage of micronutrients by the farmers by recommending the use as well as providing subsidy for Zinc sulphate, Borax and Iron sulphate.Farmers use combine harvester in a big way. This has been adopted by the farmers on their own for saving time, energy and money. They have also adopted Zero till (ZT), seed drill and rotavator. The impetus to the mechanization in agriculture has been provided by increased subsidy for tractors and other farm equipments provided by the state. Many of the extension activities of the state like MukhyamantriTeevraBeejVistarYojana, Farmers field schools on Poultry, fodder, wheat, mushroom, Kharifutsavs, Rabi utsavs, RashtriyaKrishiVikasYojana, Integrated scheme on oilseeds, pulses and maize (ISOPOM), MukhyamantriBaghwani Mission, Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) has been implemented by the district Agriculture Department and the Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA). The district faced two drought condition and the KVK prepared contingent plans for the district. It also assessed the severity of the drought condition and the available measures to overcome its adverse effects. The KrishiVigyan Kendra provides technological support to the line departments and actively participates in the various events organized by them for the farmers. Seed treatment and balanced fertilizer usage as well as the System of Rice Intensification (SRI) have been popularized among farmers. KVK, Buxar also conducted 3 batches (30 nos. in each batch) of training programmes for the kisansalahkars for providing trained manpower to the district workforce working at the grass root level.
D) Major cropping systems (based on the analysis made by the KVK)
Crops Usually Grown
Kharif : Rice, Maize, Jowar, Pearl millet, Pigeon pea, Cucurbits and Okra
Rabi : Wheat, Barley, Lentil, Gram, Pea, Mustard and Rapeseed, Potato, Onion, Coriander, Cauliflower, Cabbage, Linseed
Summer : Vegetables, Mentha, Moong
| S.N. | Major cropping system in Buxar district |
|---|---|
| 1 | Rice-wheat |
| 2 | Rice-chickpea |
| 3 | Rice-lentil |
| 4 | Rice-onion |
| 5 | Rice-mustard |
| 6 | Rice-mustard-moong |
| 7 | Rice-cabbage/cauliflower |
| 8 | Rice-mentha |
| 9 | Maize cob-potato-wheat |
| 10 | Maize-tomato |
| 11 | Maize-potato |
| 12 | Okra-cabbage/cauliflower |
| 13 | Bajra-chickpea |
Description of Agro-climatic Zone & major agro ecological situations (based on soil and topography)
| S.N. | Agro-climatic Zone | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | III B | Irrigated /Rainfed plain, Diara |
| S.N. | Agro Ecological Situation | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | (Block-Navanagar, Buxar, Itarhi, Dumraon&Chausa) | Irrigated Plain Area |
| 2 | (Block- Simri, Rajpur, Keshath,Chausa , Chaugain) | Rain fed plain Area |
| 3 | (Block- Brahmapur, Chakki, Simri, Buxar) | Diara Area |
Area, Production and Productivity of major crops cultivated in the district
| S.N. | Crop | Area (ha) | Production (q) | Productivity (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rice | 109392 | 304437936.0 | 2783.0 |
| 2 | Wheat | 81532 | 128494432.0 | 1576.0 |
| 3 | Gram | 4100 | 2968400.0 | 724.0 |
| 4 | Lentil | 5400 | 2484000.0 | 460.0 |
| 5 | Maize | 4278 | 6378498.0 | 1491.0 |
| 6 | Barley | 1363 | 1232152.0 | 904.0 |
| 7 | Mustard/Tori | 3000 | 2325000.0 | 775.0 |
| Linseed | 321 | 276.0 | 860.0 | |
| 8 | Coarse Cereals | 5285 | 5532.0 | 1047 |
| 9 | Arhar | 465 | 928605.0 | 1997.0 |
| 10 | Khesari | 4965 | 2085.0 | 420.0 |
| 11 | Moong | 300 | 235500.0 | 785.0 |
| 12 | Spice & Condiments | 6 | - | 833 |
| 13 | Total Fruits & Vegetables | 2908 | - | 1828 |
| 14 | Total Oilseeds | 1328 | - | 795 |
| 15 | Total Non-Food Crops | 1328 |
Production and Productivity of Livestock and Poultry
| Category | Population (000) | Productivity |
|---|---|---|
| Non descriptive Cattle (local low yielding) | 119697 | 480 litres/lactation |
| Improved cattle | 29.245 | 640 litres/ lactation |
| Crossbred cattle | 57954 | 1800 litres/lactation |
| Non descriptive Buffaloes (local low yielding) | 189293 | 1440 litres/lactation |
| Descript Buffaloes | 8.544 | 1550 litres/lactation |
| Goat | 71033 | |
| Sheep | 22487 | |
| Others (Pig etc.) | 12495 | |
| Poultry (Commercial) | 112.963 (no. of birds in 000) | 85 eggs per year |
| Poultry (Backyard) | 37.950 (no. of birds in 000) | Only broiler farms exist |
| Fisheries | 642 (No. of Reservoirs) |
E) Weather data
Buxar on the whole, endowed with congenial climatic conditions for cultivation of wide range of crops and trees. The three zones have little variation in climate, having hot summer, wet monsoon, and dry cool winter with maximum temperature reaching above 400C in June. The minimum temperature reaches below 50C in January.The average annual rainfall in the Buxar District is 994 mm. As vast tracts of land are rainfed slight decrease in rainfall decreases the cropping intensity in the district and threatens the livelihoods of the farmers.
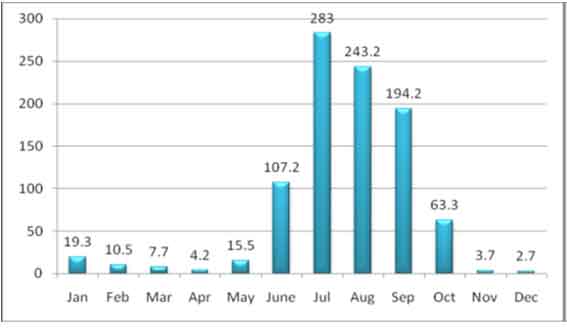
Mean annual rainfall (mm)
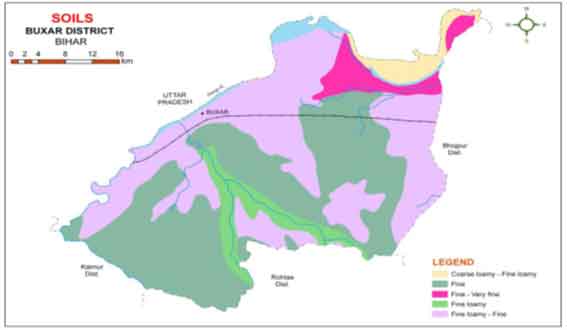
Soil type and characteristics in Buxar district
| S.N. | Soil Type | Area (‘000 ha) | % of total | Characteristics | Blocks | Deficient Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sandy Loam | 56.1 | 39.2 | Low water holding capacity, low organic matter | Simri, Chausa, Dumraon, Chakki and Brahmpur | NPK, Zn, B, Fe |
| 2 | Loam | 20.1 | 14.0 | Low water holding capacity, low organic matter | Dumraon, Keshath, Chaugain and Buxar | NP, Zn, B |
| 3 | Loamy Clay | 48.4 | 33.8 | Medium water holding capacity, low organic matter | Itarhi, Navanagar, | N, Zn, B |
| 4 | Clay | 18.3 | 12.8 | Good water holding capacity, high organic matter | Rajpur and Navanagar | Zn, B |
Soil map of Buxar district